Solar Power Boom in Pakistan
By Riaz Haq
CA

Falling solar panel prices and soaring rates for grid electricity are driving a renewable power boom in Pakistan. A second factor spurring the growth in clean energy installations is the requirement of major Western apparel brands for garments and textile manufacturers to switch to clean energy . As a result, solar panel imports in Pakistan jumped from 2,800 MW in 2022 to 5,000 MW in 2023, despite stringent import controls imposed by the government. Solar imports are on track to reach 12,000 MW in 2024, according to solar installers. The total current installed generation capacity in Pakistan is around 40,000 MW. Grid electricity demand in Pakistan plunged in 2023 by nearly a sixth and a decline in 2024 would mark the first time in 16 years that annual electricity use has fallen consecutively, data from energy think tank Ember showed, according to Reuters .
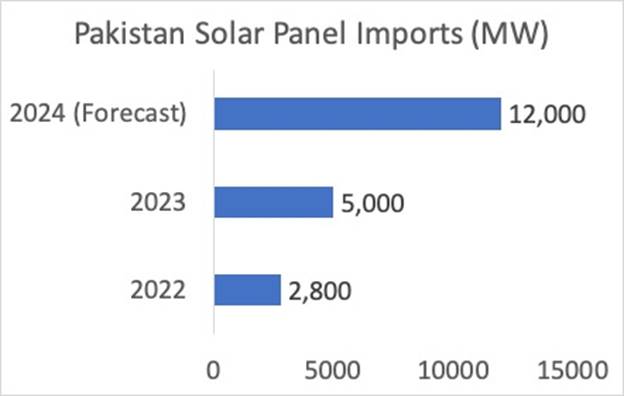
|
Pakistan Solar Panel Imports - Source PV Magazine |
Omar Malik, the CEO of Shams Power, a major solar system contractor in Pakistan, was recently quoted by PV Magazine as saying: “In 2022, 2.8 GW of solar panels were imported into Pakistan. In 2023, about 5 GW, despite the import controls, and this year the prediction is for up to 12 GW”.
Aamir Hussain, chairman Pakistan Alternative Energy Association, told Arab News that solar panels of around 1,800 MW were purchased and installed last year, which was expected to jump to 3,000 MW this year due to the lower prices of the panels and increased customer demand.
“Pakistan will be spending over $3.5 billion [this year] on solar panel imports only as this doesn’t include import of batteries, inverters and other auxiliary items,” Hussain said. “Pakistan needs to follow consistent policies regarding renewable energy to meet its national and international obligations for the greenhouse gas emissions.”
Japanese publication Nikkei Asia recently reported seeing residential building rooftops covered with solar panels in Islamabad. It also reported the proliferation of rooftop solar in small towns and villages across the country. In particular, the Nikkei story mentioned the remote village of Kardigap with a population of 5,000, in Balochistan province, where solar panels are becoming more common on the rooftops of houses.
Responding to Western apparel brands' demand for sustainability, a number of large Pakistani textile manufacturers are switching to clean energy, particularly solar. Tayyab Group of Industries (TGOIs), a major textile manufacturer, has recently signed an MOU to install a 20 MW solar system for its needs. Gul Ahmed Textile Mills Limited announced recently that it will install a 17.1 MW roof-top solar power plant to meet its energy needs.
While rapid uptake of solar is good news for the planet, it does create a major fiscal issue for the Pakistani government struggling to pay for power produced by the independent power producers ( IPPs ). The IPPs, many of them Chinese, secured a guaranteed return on investment indexed to the US dollar, plus payment for fixed capacity charges -- covering their debt servicing and other fixed costs -- regardless of whether the power plants are operational, according to Nikkei Asia. As the demand for the grid power from the IPPs declines with rising solar, the taxpayers are still on the hook for the unused installed capacity charges running into billions of dollars. Higher power tariffs and taxes will only make the situation worse.
Capping Net Metering power and reducing payments for supplying excess power to the grid is not going to solve the problem either. It will only encourage more consumers to switch to rooftop solar and use less electricity from the grid. Self consumption of the rooftop solar power saves significant energy costs for the consumer.
It seems the only way forward for the Pakistan government is to renegotiate the terms with the IPPs to significantly reduce grid power costs to address the growing cost gap between rooftop solar and the grid power.
(Riaz Haq is a Silicon Valley-based Pakistani-American analyst and writer. He blogs at www.riazhaq.com)

